What Tools And Technologies Are Used To Build Best NLI Applications?
This article is the third and last part of the series of articles – starting with NLI (Natural Language Interface) – Advantages & Dis-advantages and next Types of applications implementing NLI.
All the articles in this series are written from the perspective of the end user of an NLI.
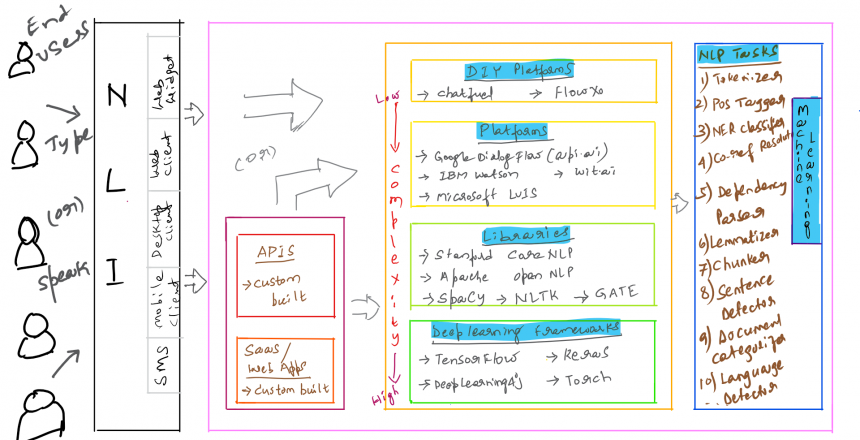
In this article, few generalizations were made in grouping the assorted Tools (as listed in the featured graphic above) to facilitate a simplified understanding.
The overarching technology that is used to build NLI (Natural Language Interface) based applications is Natural Language Processing (NLP), which is the part of Artificial Intelligence that deals with language.
The Tools are grouped as:
- Do It Yourself (DIY) Platforms
- Platforms – mostly API endpoints that accept and process a text input
- Traditional Libraries
- Deep Learning Libraries
Typically a user either types or speaks in natural language through an NLI, which could be:
- in a web widget – e.g., a text box and a select list provided by most of the Chatbots to type queries or select items from the list
- in a web browser client – e.g., Google Search box with Mic
- in a Desktop client – e.g., Cortana’s textbox and Mic in Microsoft Windows OS
- in a mobile app
- an SMS
- a headless speaker – e.g., Amazon Echo
In most of applications that implement an NLI (Natural Language Interface), the text entered is sent either to the custom APIs/ SaaS/ Web apps/ Web services or directly to the platforms for processing.
When using the Traditional or Deep Learning libraries, a Server API or a SaaS or a Web app is developed and deployed to receive/send the text through NLI – both for pre and post processing. However, for platforms like IBM Watson or Google’s DialogFlow, creating such Server APIs etc.. is optional – as the API endpoints in these platforms can be called directly from within the client application which is implementing an NLI.
The processing done to understand the text, which is mostly sent through an NLI, is what is called as Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Several disparate NLP (Natural Language Processing) tasks or components are built and deployed to understand the text. For e.g., a POS Tagger can understand and tag a text like William Jefferson as a Proper Noun.
In most cases, the text is specific to the application domain. Hence the need to build one or more of these Natural Language Processing (NLP) components (for e.g., Classifier) that is specific to the application domain.
While most of the NLP components could be built using rules of the respective language (Grammar), nevertheless, they can also be built and extended using Deep Learning platforms with Word Vectors.
Deep Learning platforms use advanced Machine Learning algorithms to build some of these NLP components (mostly text classifiers).
For an example of how a contextual Chatbot could be built using one such Deep Learning platform – Google’s TensorFlow – click here.
This completes our 3-part series of articles on NLI. To summarize:
- First, we started with finding out what advantages could an NLI application bring to an organization.
- Next, we presented what types of applications are suitable or good candidates for implementing an NLI.
- Finally, what Tools with varying degree of Complexity are being used to build applications that implement an NLI(Natural Language Interface).
I hope that our 3-part series facilitated a good understanding of an NLI and also, might have helped you in enriching your perspective on AI(Artificial Intelligence) and Machine Learning.
PL use the comments section in this post for your questions or suggestions or anything you’ve to say or want to know more about NLI or the underlying NLP technology.